Brain
What do chakras and addictive substances have in common? The brain, is that our mind? What are emotions? These questions are addressed in the following six pages. They give in a nutshell the main routes inside the body.
Energy reproduction hazards -brain-body-behavior-hormones


 All living is arranged to exist and to continue to exist as a species.The environment is essential for the survival. All life has therefore developed systems to respond to opportunities and threats in the environment. This is largely an automatic and intuitive process, even in humans. The brain shows, what to do. To this end they give a signal to the pituitary gland, that releases a hormone which stimulates the body issues to action. The main hormones are 1. to get energy; eat 2. reproduction, love en 3. to cope danger by fighting or fleeing. The most extensive systems in our body have to do with these three 'tasks'. Furthermore, we need to drink water and get air from the environment. The systems for this are less comprehensive. This because it is a matter of life or death rather quickly, you must be near water and air. Also the body temperature depends on the environment and is regularly brought up to standard. The scheme of all these things happen from the middle of the brain, in the meso-corticolimbic system. The way things are addressed within the different systems is comparable with those of our animal ancestors. Animals have in fact systems for these functions too, in part similar to human, partly different, adapted to the opportunities and dangers in their environment
All living is arranged to exist and to continue to exist as a species.The environment is essential for the survival. All life has therefore developed systems to respond to opportunities and threats in the environment. This is largely an automatic and intuitive process, even in humans. The brain shows, what to do. To this end they give a signal to the pituitary gland, that releases a hormone which stimulates the body issues to action. The main hormones are 1. to get energy; eat 2. reproduction, love en 3. to cope danger by fighting or fleeing. The most extensive systems in our body have to do with these three 'tasks'. Furthermore, we need to drink water and get air from the environment. The systems for this are less comprehensive. This because it is a matter of life or death rather quickly, you must be near water and air. Also the body temperature depends on the environment and is regularly brought up to standard. The scheme of all these things happen from the middle of the brain, in the meso-corticolimbic system. The way things are addressed within the different systems is comparable with those of our animal ancestors. Animals have in fact systems for these functions too, in part similar to human, partly different, adapted to the opportunities and dangers in their environment
Meso-corticolimbic-system-circuits/body axes
The pituitary gland hangs from the mesocortico-limbic system. It retrieves information from the rest of the brain. There are experiences of the past in the memory with a label: 'successfull' or 'unsuccessfull': nice or nasty; nice or sad; something great or to get angry, or afraid of . We experience these labels in the form of emotions, although the experience of 'nice' or 'nasty' is usually not called an emotion. Emotions are the language of the body itself mainly linked to experiences in the field of love or of hazards. If there is a chance that one later in life has many dangers to face, then one gets from inside-out the incentive to practice already at a young age, this exercise with danger and excitement, sometimes even provoked by the person himself, will receive a positive emotional "reward". Thus an extensive repertoire develops, which later will come in handy. Gradually prefrontal lobes get more and more control over the emotional behavior and one gets more self-imposed rules. These lobes reach maturity on the age of 24.
Grow during sleep  The epiphysis is more in the back of the brain than the pitiutary. It gives sleep hormone. We sleep every day to sort and organize experiences, while no more new experiences come in between. After sorting, the body can grow, strengthen or weaken brain connections, so next time we are better able to give a good response. You learn gradually what is safe and what to watch out for. But there may be more fundamental changes to take place, namely that the equilibrium ‘institutions’ of the hormone systems change themselves. The hormonal 'settings' are very precisely adjusted. That explains why you usually keep the same weight, more or less, for a long time and losing weight is so difficult. If any of the three pituitary systems come in a fix, for example when for a long period little food is available, then the brain is to customize to it. Then the body can for example set to become less active or uses another form of fat storage. Famine can change 'settings' (this is shown by examination of the effects of the Amsterdam hunger winter). It is similar to having experienced a lot of danger or stress and then becoming extra alert for hazards. Moreover it seems that the brain also without acute emergencies can adapt the 'settings' to the experiences of the past days and past. Other 'settings' lead to different behavior, even sometimes to a different 'personality'.
The epiphysis is more in the back of the brain than the pitiutary. It gives sleep hormone. We sleep every day to sort and organize experiences, while no more new experiences come in between. After sorting, the body can grow, strengthen or weaken brain connections, so next time we are better able to give a good response. You learn gradually what is safe and what to watch out for. But there may be more fundamental changes to take place, namely that the equilibrium ‘institutions’ of the hormone systems change themselves. The hormonal 'settings' are very precisely adjusted. That explains why you usually keep the same weight, more or less, for a long time and losing weight is so difficult. If any of the three pituitary systems come in a fix, for example when for a long period little food is available, then the brain is to customize to it. Then the body can for example set to become less active or uses another form of fat storage. Famine can change 'settings' (this is shown by examination of the effects of the Amsterdam hunger winter). It is similar to having experienced a lot of danger or stress and then becoming extra alert for hazards. Moreover it seems that the brain also without acute emergencies can adapt the 'settings' to the experiences of the past days and past. Other 'settings' lead to different behavior, even sometimes to a different 'personality'.
Daily
We look around to fill our needs and compare the environment with the stored previous experiences. There is usually a rhythm in which all needs are covered, which is most evident in daily sleep and getting hungry so we go to eat. This rhythm is largely determined from within, providing daily feature, but there is also influence on this from mind of the person himself and the circumstances in the area. We are less aware of emotional processes, for example, that we constantly watch if the environment is favorable or hostile to us. Yet there seems even to be an inner need to activate the emotional circuits regularly, possibly by way of exercise. This activation takes place not only by actually doing something, but can also be caused by seeing, through involvement and empathy. This explains why we like TV and movie watching and to what kind of movies we want to watch.
Chakras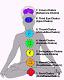
 The Oriental medicine recognizes energypoints in the body. These 'chakras' connect hormonal and neural systems. Judging from the description, the lower three chakras correspond to the three systems 1. food, 2. love and 3. threats to face. The upper four chakras integrate in various ways the bottom three. The colors associated with the chakras are used where possible to link the various systems.
The Oriental medicine recognizes energypoints in the body. These 'chakras' connect hormonal and neural systems. Judging from the description, the lower three chakras correspond to the three systems 1. food, 2. love and 3. threats to face. The upper four chakras integrate in various ways the bottom three. The colors associated with the chakras are used where possible to link the various systems.
Crown Chakra epiphysis
Forehead Chakra pituitary
Throat Chakra communications
Heart Chakra breathing, hearthbeat
Solar Plexus Chakra face danger
Sacrum Chakra sexuality, love
Basic or root chakra energy, food
Oriental wisdom is the pursuit of balance within and between the chakras.
"Suffering and pain can cause bitterness and anger, either cause wisdom:
Those who use suffering and pain for wisdom, become saints ".
That searching balance is important, will also turn out from the further neurobiological knowledge, which brnsoc. brings.
Evolution of plants and animals in their environment
Plants produce alkaloids directed to the environment, some of these biochemical substances do have the function do attract, some to destroy for example microorganisms. Like these early life forms in the evolution, also in humans and animals alkaloids appear to play a role in the interaction with the environment. 1. nicotine, 2. opiates, 3. cocaine and amphetamines 1. food, 2. love, 3 'to face danger’.
Addictive psychotropic substances 








 The nervous system of the brain is the ‘head to toe 'communication system of the body. Electro-magnetic pulses and biochemical materials ensure the transmission of signals. The addictive alkaloid psychotropic substances 1. nicotine, 2. opiates, 3. cocaine en amphetamines establish connection with the same systems as for 1. to eat, 2. love, reproduction, 3 'to face danger'. It is sometimes forgotten, but 'the body makes its own drugs'. In the meso-cortico-limbic system are important receiving points (receptors) of these systems, normally to be filled by substances from the inside. Actually, given the impact of these on-known biochemical substances, it is quite logical that they seem to play an leading role in important systems. As the 'exogenous' addictive substance fits in the same receptors as the ‘endogenous’ signal substance of whether or not successful conduct of a certain type, the substances do have their characteristic effects. The behavior that belongs to the specific system does not really necessarily have to take place to obtain the impact. So give these substances a short route without much effort to certain emotions, 1. tasty, 2. orgasmic of 3. feeling successful. A 'but ...' is of course, that as the brain itself does not recognize as coming from the outside, this means not as 'unnatural', and it is possible that the 'institutions' are going to change, changing the alignment with the environment as it was before. In all daily, cyclic systems endogenous addictive substances play a key role. For the sleep the benzodiazepines.
The nervous system of the brain is the ‘head to toe 'communication system of the body. Electro-magnetic pulses and biochemical materials ensure the transmission of signals. The addictive alkaloid psychotropic substances 1. nicotine, 2. opiates, 3. cocaine en amphetamines establish connection with the same systems as for 1. to eat, 2. love, reproduction, 3 'to face danger'. It is sometimes forgotten, but 'the body makes its own drugs'. In the meso-cortico-limbic system are important receiving points (receptors) of these systems, normally to be filled by substances from the inside. Actually, given the impact of these on-known biochemical substances, it is quite logical that they seem to play an leading role in important systems. As the 'exogenous' addictive substance fits in the same receptors as the ‘endogenous’ signal substance of whether or not successful conduct of a certain type, the substances do have their characteristic effects. The behavior that belongs to the specific system does not really necessarily have to take place to obtain the impact. So give these substances a short route without much effort to certain emotions, 1. tasty, 2. orgasmic of 3. feeling successful. A 'but ...' is of course, that as the brain itself does not recognize as coming from the outside, this means not as 'unnatural', and it is possible that the 'institutions' are going to change, changing the alignment with the environment as it was before. In all daily, cyclic systems endogenous addictive substances play a key role. For the sleep the benzodiazepines.
The group, society, religion
Many animals are not only linked together for reproduction only, but are connected as a group too. Groupanimals, including humans, don’t have necessarily only an individual survival instinct, but do often have an intuition to contribute to the survival of the family, group, community, species. The opiates are not only an important role in reproduction, but also a role in connecting with other animals or humans. A sense of belonging does develop, with whom, to whom we are safe and, negatively, to whom must we be careful. The mind plays a role, but especially the emotionality. Through religion, language and music alignment takes place (especially) on an emotional level. A linkage between neurobiology, thinking of the mind and society is to be found in Spinoza (1632-1677) and the Dutchman Coornhert (1522-1590) Man has developed the ability to direct reactions and think. This (see also Damasio) and the flexibility and variability of the human species enable mankind to influence its existence more than the animals.